Limited Mobility
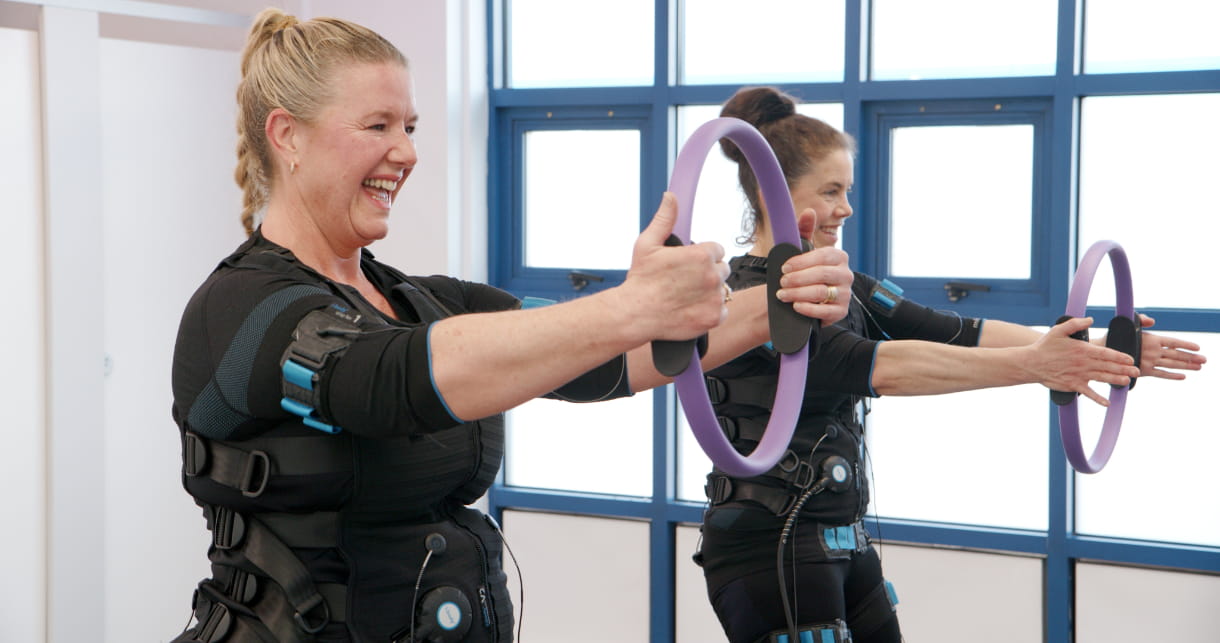

EMS is a safe and practical way to increase strength and improve fitness for those with limited mobility.
EMS (Electrical Muscle Stimulation) Training is considered an effective workout for individuals with limited mobility or those in a wheelchair. As EMS induces muscle contractions using electrical impulses it means you can build strength without putting stress or mechanical load on injured joints, ligaments or tendons. A significant advantage of EMS is that it can provide muscle activation without voluntary movement helping to prevent muscle atrophy.
EMS is a safe and practical option for those with limited mobility providing a low impact and joint friendly workout that targets deep stabilising muscles fibres, often difficult to reach with conventional exercises, to improve strength and mobility, alleviate muscle tension, improve circulation and manage pain ultimately helping to improve confidence and independence.
The majority of our studios have good access for those with limited mobility allowing them to have an EMS training session tailored to the needs and health status of the individual in a private setting.
Please note that EMS training is not suitable for the following:
- Individuals with implanted medical devices such as pacemakers.
- People with severe neurological disorders or epilepsy.
- Those with severe heart or aortic disease such as cardiac arrhythmias, thrombosis, or recent heart attacks.
- It is generally prohibited for pregnancy.
- Anyone with acute illness or infection.
- People with cancer.
- Those with inguinal or abdominal hernias.
- Anyone with chronic disease such as metabolic disease, respiratory conditions, or autoimmune diseases.
- Immediately following surgery (often requires an 8 week wait).
- Those with a risk of rhabdomyolysis due to muscle damage.